Choose the statements that are true about the gut microbiota: it is a complex and diverse community of microorganisms that reside in the human gut. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining overall human health, influencing everything from immune function to metabolism.
Understanding the gut microbiota and its impact on human health is a rapidly growing field of research, with potential implications for disease prevention and treatment.
In this article, we will explore the composition and diversity of the gut microbiota, discuss its role in human health and disease, and review the different methods used to study the gut microbiota. We will also explore the concept of personalized medicine in the context of the gut microbiota and discuss the potential for using gut microbiota analysis to tailor medical treatments to individual patients.
Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity
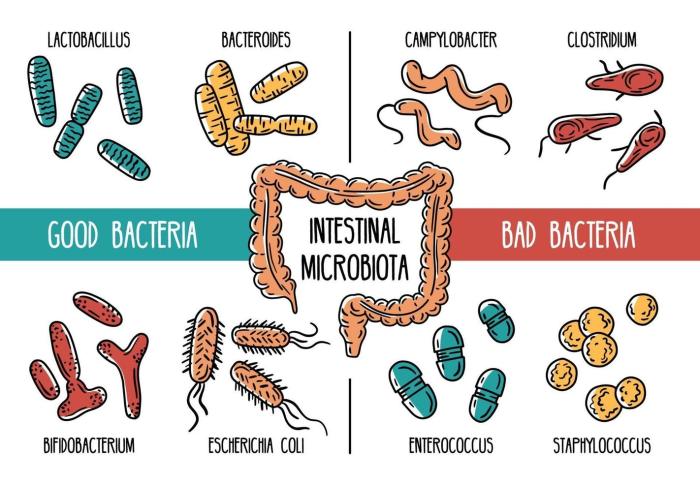
The gut microbiota is a complex community of trillions of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, that reside in the human gastrointestinal tract. These microbes play a crucial role in maintaining overall human health and well-being.
Bacterial Composition
- The dominant bacterial phyla in the human gut are Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes.
- Other common phyla include Proteobacteria, Actinobacteria, and Fusobacteria.
- The composition of the gut microbiota varies between individuals and is influenced by factors such as diet, age, and environment.
Viral Composition
- Viruses are the most abundant microorganisms in the gut microbiota.
- They play a role in regulating the immune system and protecting against pathogens.
- The composition of the gut virome is less well-studied than the bacterial microbiome.
Fungal Composition
- Fungi are a relatively minor component of the gut microbiota.
- They include yeasts, molds, and filamentous fungi.
- Fungi contribute to nutrient metabolism and immune function.
Diversity
The diversity of the gut microbiota is influenced by various factors, including:
- Diet:A diet rich in fiber and fermented foods promotes a diverse microbiota.
- Age:The microbiota composition changes with age, with a decrease in diversity observed in older adults.
- Environment:Exposure to environmental factors, such as antibiotics and pollution, can alter the gut microbiota composition.
Gut Microbiota and Human Health
The gut microbiota plays a vital role in maintaining overall human health by contributing to:
Immune Function
- The gut microbiota educates the immune system and helps distinguish between harmful and beneficial microorganisms.
- It produces antimicrobial peptides and other molecules that protect against pathogens.
Metabolism
- The gut microbiota assists in the digestion and absorption of nutrients.
- It produces vitamins and other essential compounds that the body cannot synthesize on its own.
Nutrient Absorption
- The gut microbiota helps break down complex carbohydrates and proteins into smaller molecules that can be absorbed by the body.
- It also produces enzymes that enhance the absorption of minerals, such as calcium and iron.
Potential Health Implications of Imbalances
Imbalances in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, have been linked to various health conditions, including:
- Inflammatory bowel disease
- Obesity
- Type 2 diabetes
- Autism spectrum disorder
Gut Microbiota and Disease: Choose The Statements That Are True About The Gut Microbiota

Gut microbiota imbalances have been implicated in the development and progression of various diseases:
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Dysbiosis has been observed in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- The gut microbiota may contribute to inflammation and tissue damage in these conditions.
Obesity, Choose the statements that are true about the gut microbiota
- Individuals with obesity tend to have a different gut microbiota composition compared to lean individuals.
- The gut microbiota may influence energy metabolism and body weight regulation.
Type 2 Diabetes
- Dysbiosis has been linked to insulin resistance and impaired glucose metabolism.
- The gut microbiota may play a role in the development of type 2 diabetes.
Therapeutic Potential
Manipulating the gut microbiota through interventions such as probiotics, prebiotics, and fecal microbiota transplantation holds promise as a therapeutic strategy for preventing and treating certain diseases:
- Probiotics: Live microorganisms that confer health benefits when consumed.
- Prebiotics: Non-digestible substances that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
- Fecal microbiota transplantation: Transfer of healthy gut microbiota from a donor to a recipient.
Gut Microbiota Research Methods
Various methods are used to study the gut microbiota:
Culture-Dependent Methods
- Traditional culture:Isolating and growing bacteria on agar plates.
- Anaerobic culture:Culturing bacteria under oxygen-limiting conditions.
Culture-Independent Methods
- 16S rRNA gene sequencing:Sequencing a specific region of the bacterial genome to identify and quantify different bacterial species.
- Metagenomics:Sequencing all the DNA in a sample to obtain a comprehensive view of the entire microbial community.
- Metatranscriptomics:Sequencing RNA to study the active genes and pathways within the microbial community.
Advantages and Limitations
Each method has its advantages and limitations:
- Culture-dependent methods:Can provide pure isolates for further characterization but may underestimate the diversity of the gut microbiota.
- Culture-independent methods:Provide a more comprehensive view of the microbial community but may have limitations in species identification and functional analysis.
Gut Microbiota and Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine aims to tailor medical treatments to individual patients based on their unique characteristics, including their gut microbiota:
Gut Microbiota Analysis
- Analyzing an individual’s gut microbiota composition can provide insights into their health status and disease risk.
- This information can be used to develop personalized treatment plans.
Tailored Interventions
- Probiotic or prebiotic supplements can be selected based on an individual’s gut microbiota profile.
- Fecal microbiota transplantation may be considered for individuals with severe dysbiosis.
Improved Patient Outcomes
Personalized medicine approaches that incorporate gut microbiota analysis have the potential to improve patient outcomes by:
- Enhancing treatment efficacy
- Reducing adverse effects
- Preventing disease progression
FAQ Guide
What is the gut microbiota?
The gut microbiota is a complex and diverse community of microorganisms that reside in the human gut. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, and fungi.
What is the role of the gut microbiota in human health?
The gut microbiota plays a vital role in maintaining overall human health. These microorganisms help to digest food, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful bacteria.
How can I improve my gut microbiota?
There are a number of things you can do to improve your gut microbiota, including eating a healthy diet, getting enough exercise, and reducing stress.