Pal cadaver axial skeleton skull lab practical question 1 delves into the intricate world of human anatomy, offering a unique opportunity to examine the skull and axial skeleton firsthand. This practical exercise provides invaluable insights into the structure and function of these essential body parts.
Through a comprehensive examination of the skull’s components, regions, and their functions, students gain a profound understanding of the protective role it plays in housing the brain and sensory organs. Additionally, the exploration of the axial skeleton, including the vertebral column, ribs, and sternum, sheds light on their crucial role in supporting the body, protecting vital organs, and facilitating movement.
1. Skull Anatomy: Pal Cadaver Axial Skeleton Skull Lab Practical Question 1
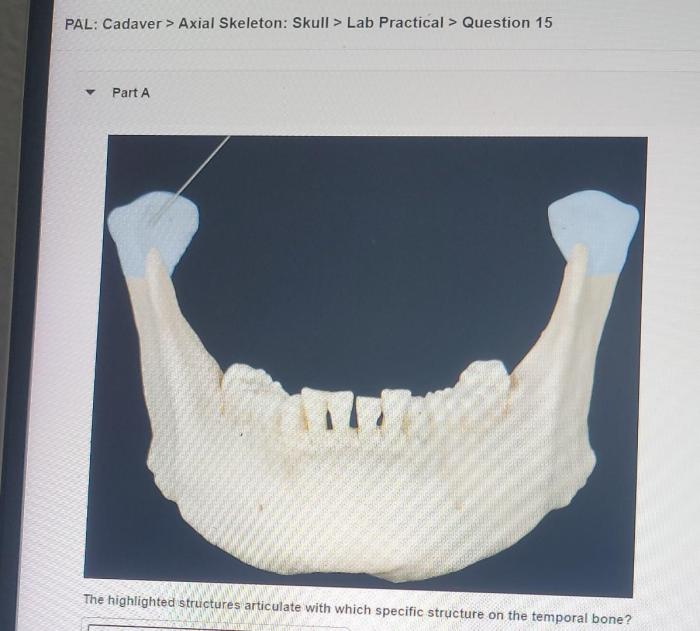
The skull is a complex structure that forms the bony framework of the head. It consists of 22 bones that are joined together by immovable joints called sutures. The skull is divided into two main regions: the cranium and the facial skeleton.
Bones of the Cranium
- Frontal bone
- Parietal bones (2)
- Temporal bones (2)
- Occipital bone
- Sphenoid bone
- Ethmoid bone
Bones of the Facial Skeleton
- Nasal bones (2)
- Maxillary bones (2)
- Zygomatic bones (2)
- Lacrimal bones (2)
- Palatine bones (2)
- Inferior nasal conchae (2)
- Vomer bone
- Mandible
Regions of the Skull
The cranium is the upper part of the skull that encloses the brain. The facial skeleton is the lower part of the skull that forms the face.
2. Axial Skeleton
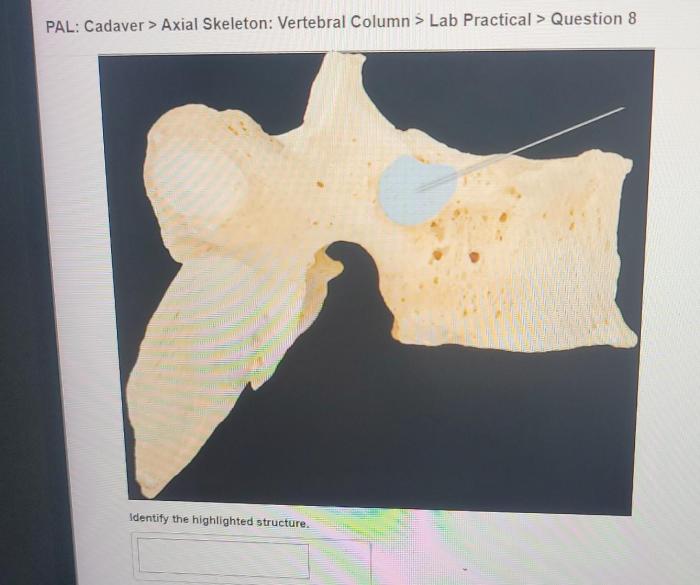
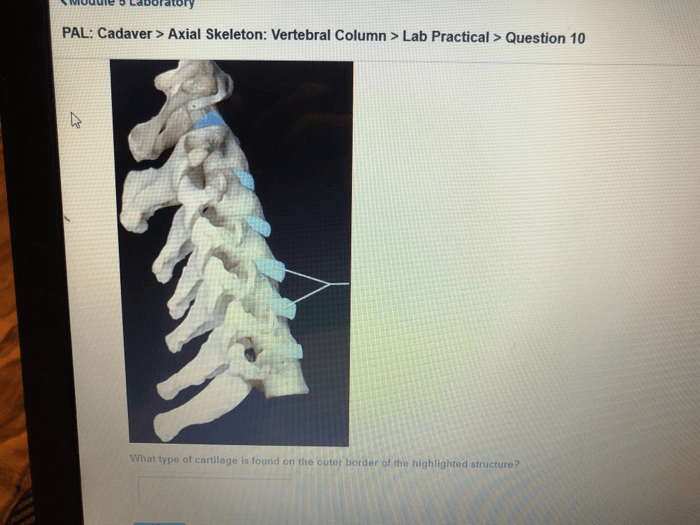
Components of the Axial Skeleton
- Vertebral column
- Ribs (12 pairs)
- Sternum
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column is a flexible, segmented structure that extends from the base of the skull to the pelvis. It consists of 33 vertebrae that are divided into five regions: cervical (7), thoracic (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5), and coccygeal (4).
Ribs and Sternum
The ribs are 12 pairs of long, curved bones that extend from the thoracic vertebrae. They form the rib cage, which protects the thoracic cavity and its contents (heart, lungs, and esophagus).
The sternum is a flat, midline bone that forms the anterior part of the rib cage. It is connected to the ribs by cartilage.
3. Cadaver Lab Practical
Examination of the Skull
- Identify the major bones of the cranium and facial skeleton.
- Examine the sutures that join the bones together.
- Locate the foramina and fissures for the passage of nerves and blood vessels.
Examination of the Axial Skeleton
- Identify the different regions of the vertebral column.
- Examine the structure of a typical vertebra.
- Locate the intervertebral discs and facet joints.
- Examine the ribs and sternum.
Safety Precautions
- Wear gloves and a lab coat.
- Handle the cadaver with respect.
- Do not use sharp instruments near the cadaver.
4. Pal Cadaver
Importance of Pal Cadavers
Pal cadavers are invaluable for anatomical study because they provide a realistic and detailed view of the human body. They allow students to learn about the structure and function of the human body in a hands-on way.
Ethical Considerations, Pal cadaver axial skeleton skull lab practical question 1
The use of cadavers for research and education is governed by strict ethical guidelines. These guidelines ensure that the bodies are treated with respect and that the donors’ wishes are honored.
Benefits and Challenges
Using pal cadavers in anatomy labs has several benefits. These benefits include:
- Provides a realistic and detailed view of the human body
- Allows students to learn about the structure and function of the human body in a hands-on way
- Helps students develop their anatomical knowledge and skills
However, there are also some challenges associated with using pal cadavers. These challenges include:
- Can be emotionally difficult for some students
- Requires a significant amount of time and resources
- Can be difficult to obtain
Answers to Common Questions
What is the significance of using a pal cadaver in anatomy labs?
Pal cadavers provide an invaluable opportunity to study human anatomy firsthand, allowing students to gain a deeper understanding of the intricate structures and relationships of the human body.
What ethical considerations should be taken into account when using cadavers for research and education?
The use of cadavers for research and education raises ethical concerns regarding respect for the deceased and their families, informed consent, and the proper handling and disposal of human remains.
What are the benefits and challenges of using pal cadavers in anatomy labs?
Benefits include providing students with a realistic and comprehensive learning experience, while challenges include the emotional and psychological impact on students and the need for proper facilities and training.
