Genetic transfer in bacteria prevent the rise of superbugs – Genetic transfer in bacteria plays a pivotal role in the emergence and spread of superbugs, bacteria that are resistant to multiple antibiotics. This article delves into the mechanisms of genetic transfer, its impact on the rise of superbugs, and strategies to prevent their spread, offering insights into the importance of ongoing research and innovation in combating this pressing global health threat.
Mechanisms of Genetic Transfer in Bacteria
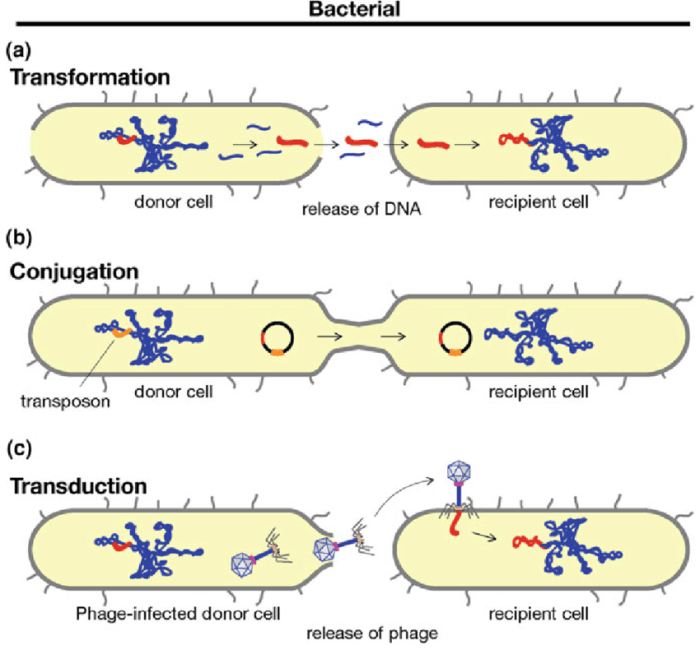
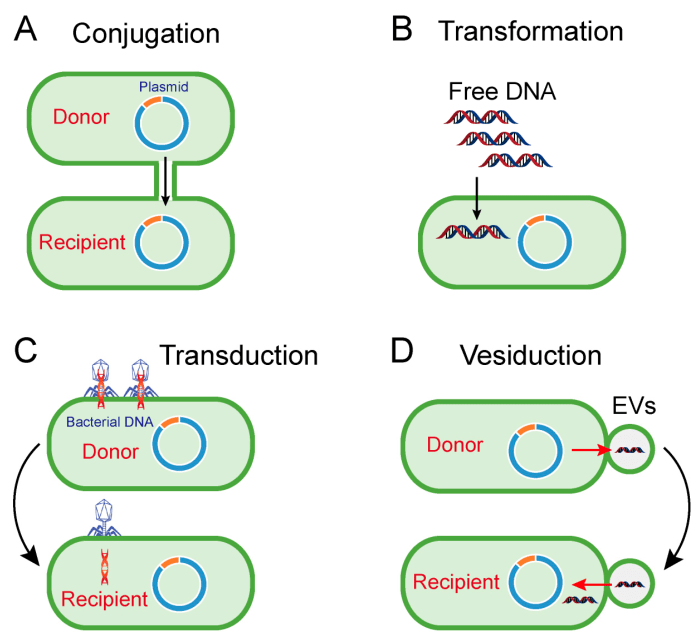
Genetic transfer is the process by which bacteria exchange genetic material with each other. This can occur through three main mechanisms: transformation, conjugation, and transduction.
Transformation, Genetic transfer in bacteria prevent the rise of superbugs
Transformation is the process by which bacteria take up DNA from the environment. This can occur when bacteria are exposed to DNA that has been released from other bacteria that have lysed (burst open). The DNA can then be integrated into the recipient bacteria’s genome, providing it with new genes.
Transformation is a common mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes. For example, the gene that confers resistance to the antibiotic penicillin has been shown to be transferred between bacteria through transformation.
Conjugation
Conjugation is the process by which bacteria exchange genetic material through direct cell-to-cell contact. This is mediated by a plasmid, which is a small, circular piece of DNA that is not essential for the survival of the bacteria.
Plasmids can carry genes that confer antibiotic resistance. When bacteria conjugate, the plasmid can be transferred from one bacteria to the other, providing the recipient bacteria with the antibiotic resistance genes.
Transduction
Transduction is the process by which bacteria exchange genetic material through the action of a virus. The virus infects one bacteria and incorporates some of its DNA into its own genome. The virus then infects another bacteria and transfers the DNA to the new host.
Transduction can also be a mechanism for the spread of antibiotic resistance genes. For example, the gene that confers resistance to the antibiotic erythromycin has been shown to be transferred between bacteria through transduction.
Impact of Genetic Transfer on the Rise of Superbugs
Genetic transfer plays a major role in the emergence and spread of superbugs, bacteria that are resistant to multiple antibiotics. This is because genetic transfer can allow bacteria to acquire antibiotic resistance genes from other bacteria.
The acquisition of antibiotic resistance genes can lead to the development of untreatable infections. For example, the emergence of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus(MRSA) is due to the acquisition of a gene that confers resistance to methicillin, a commonly used antibiotic.
The spread of antibiotic resistance genes through genetic transfer is a major public health concern. It is estimated that antibiotic resistance causes at least 23,000 deaths in the United States each year.
Strategies to Prevent the Rise of Superbugs: Genetic Transfer In Bacteria Prevent The Rise Of Superbugs
There are a number of strategies that can be used to prevent the spread of genetic transfer in bacteria and the rise of superbugs.
- Infection control measures: Infection control measures, such as handwashing and the use of personal protective equipment, can help to prevent the spread of bacteria from one person to another.
- Antibiotic stewardship: Antibiotic stewardship programs are designed to ensure that antibiotics are used appropriately and only when necessary. This can help to reduce the selection pressure for antibiotic resistance.
- Development of new antibiotics: The development of new antibiotics is essential for combating the rise of superbugs. New antibiotics can be used to treat infections that are resistant to existing antibiotics.
Role of Research and Innovation
Ongoing research and innovation are essential for understanding and preventing genetic transfer in bacteria. This research can lead to the development of new strategies to prevent the spread of antibiotic resistance genes and the rise of superbugs.
One promising area of research is the development of new technologies, such as CRISPR-Cas systems, that can be used to target and destroy specific genes. This technology could be used to develop new antibiotics that are effective against superbugs.
FAQ Explained
What are the mechanisms of genetic transfer in bacteria?
Genetic transfer in bacteria can occur through transformation, conjugation, and transduction.
How does genetic transfer contribute to the rise of superbugs?
Genetic transfer allows bacteria to acquire antibiotic resistance genes, leading to the development of superbugs that are resistant to multiple antibiotics.
What strategies can be implemented to prevent the rise of superbugs?
Strategies to prevent the rise of superbugs include infection control measures, antibiotic stewardship, and the development of new antibiotics.